A better education, an opinion
Oct 31th 2022
I subscribe to the approach of this group of principles in Education, that reconciles very well known notions in science and epistemology.
Note aside: to the people who share the meaning of this day, Happy Halloween day!
The "Four Cs" are:
Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
Communication (Socialization)
Collaboration (Teamwork)
Creativity and Innovation
References:
1) P21: Partnership for 21st Century Learning. (2015). P21 framework definitions. The Partnership for 21st century learning, 1-9.(accesed October 31, 2022).
2) Van Roekel, D., & National Education Association. (2014). Preparing 21st century students for a global society: an educator’s guide to the “Four Cs.”. National Education Association.
3) Bennett, N., Dunne, E., & Carré, C. (2000). Skills Development in Higher Education and Employment. Taylor & Francis, Inc., 7625 Empire Dr., Florence, KY 41042.
4) Bellanca, J. A. (Ed.). (2010). 21st century skills: Rethinking how students learn. Solution tree press.
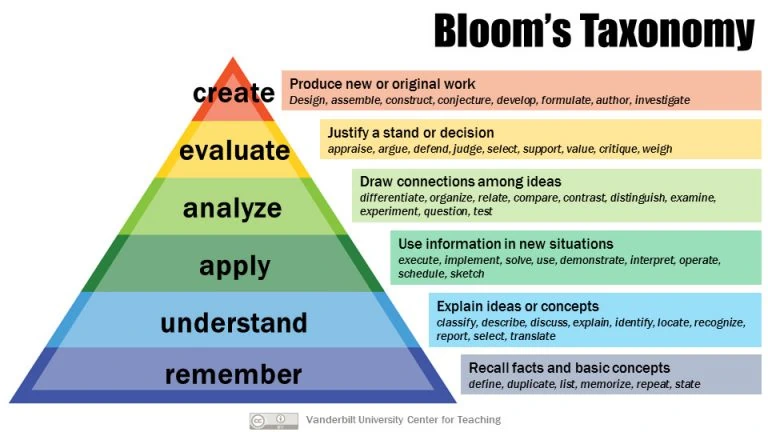
The "Bloom's Educational Goals Taxonomy".
A continuum framework
(From top to bottom):
Create
Evaluate
Analyze
Apply
Understand
Remember
Knowledge “involves the recall of specifics and universals, the recall of methods and processes, or the recall of a pattern, structure, or setting.”
Comprehension “refers to a type of understanding or apprehension such that the individual knows what is being communicated and can make use of the material or idea being communicated without necessarily relating it to other material or seeing its fullest implications.”
Application refers to the “use of abstractions in particular and concrete situations.”
Analysis represents the “breakdown of a communication into its constituent elements or parts such that the relative hierarchy of ideas is made clear and/or the relations between ideas expressed are made explicit.”
Synthesis involves the “putting together of elements and parts so as to form a whole.”
Evaluation engenders “judgments about the value of material and methods for given purposes.”
Comprehension “refers to a type of understanding or apprehension such that the individual knows what is being communicated and can make use of the material or idea being communicated without necessarily relating it to other material or seeing its fullest implications.”
Application refers to the “use of abstractions in particular and concrete situations.”
Analysis represents the “breakdown of a communication into its constituent elements or parts such that the relative hierarchy of ideas is made clear and/or the relations between ideas expressed are made explicit.”
Synthesis involves the “putting together of elements and parts so as to form a whole.”
Evaluation engenders “judgments about the value of material and methods for given purposes.”
Remember
Recognizing
Recalling
Understand
Interpreting
Exemplifying
Classifying
Summarizing
Inferring
Comparing
Explaining
Apply
Executing
Implementing
Analyze
Differentiating
Organizing
Attributing
Evaluate
Checking
Critiquing
Create
Generating
Planning
Producing
Recognizing
Recalling
Understand
Interpreting
Exemplifying
Classifying
Summarizing
Inferring
Comparing
Explaining
Apply
Executing
Implementing
Analyze
Differentiating
Organizing
Attributing
Evaluate
Checking
Critiquing
Create
Generating
Planning
Producing
References:
1) Anderson, L. W., Krathwohl, D. R., Bloom, B. S., & Bloom, B. S. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: Complete Edition. Pearson Longman.
2) Armstrong, P. (2016). Bloom’s taxonomy. Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching.


